High-power electric molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements for element temperatures up to 1850°CMoSi2 heating elements are available as straight or bent elements in a wide range of shapes and sizes, all characterized by long life and consistent performance. Low energy consumption Flexible designs Wide variety of grades
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are resistance type heating elements made of a dense ceramic-metallic material which can produce furnace temperatures approaching 1800°C. Although more expensive than traditional metallic elements, MoSi2 elements are known for their longevity due in part to a protective quartz layer that forms on the surface of the element “hot zone” during operation. Duralite MoSi2 elements are made to industry standard established resistance values, dimensions and geometries, and therefore are interchangeable with other manufacturers of molybdenum disilicide elements. The key difference between Duralite MoSi2 and other MoSi2 suppliers is that Duralite MoSi2 elements are exceptionally priced. Duralite MoSi2 elements are graded in two maximum temperature ranges of 1700°C (3090°F) and 1800°C (3270°F). Elements are available in many shapes and forms (see examples shown below). Specifically, we offer the following MoSi2 styles: “U-shaped” (most common), “W-shaped”, and “Straight-shaped”, with or without right angle or oblique angle bends. Each element is specified by a “hot zone” diameter (d1) and length (Le), and a “cold zone” diameter (d2) and length (Lu).
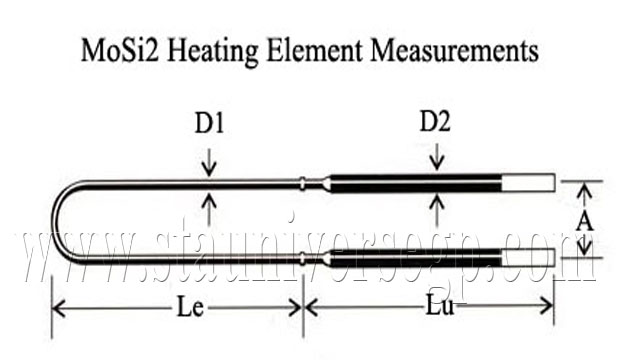
Examples of typical MoSi2 element configurations.
3/6mm | d1=3mm | d2=6mm | A=25-30mm |
6/12mm | d1=6mm | d2=12mm | A=30-50mm |
7/14mm | d1=7mm | d2=14mm | A=30-50mm |
9/18mm | d1=9mm | d2=18mm | A=35-60mm |
12/24mm | d1=12mm | d2=24mm | A=60-100mm |
Benefits of MoSi2 elements include high temperature operation (in air), long element life and the ability in some cases to replace any failed elements hot.
Customers of Duralite MoSi2 elements enjoy two key added benefits – first, unparalleled price and second, experienced engineering support. Anyone can sell MoSi2, but knowing how to design the system is where Duralite excels. MoSi2 systems must be engineered for customer to get the best performance and optimum service life. Duralite engineers can assist in:
· analyzing the relationship between the furnace temperature, element temperature and the element surface load
· selecting the element surface load according to the furnace construction, atmosphere and operating temperature
· choosing the most suitable element size and style for your application
Physical Properties:
Bulk Density-g/cm3 | Bending Strength-MPa | Hardness-GPa | Compression Strength-MPa | Water Absorption-% | Heated Elongation-% |
5.8±0.1 | 450 | 11 | >1500 | ≤0.2% | 4 |
Different Working Temperature in Different Atmosphere.
Atmosphere | The Maximum Using Temperature of Element | |
1700 Grade | 1800 Grade | |
NO2,CO2,O2,Air | 1700°C | 1800°C |
He,Ar,Ne | 1650°C | 1750°C |
SO2 | 1600°C | 1700°C |
CO,H2 | 1500°C | 1600°C |
WetH2 | 1400°C | 1500°C |
DryH2 | 1350°C | 1450°C |
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are resistance type heating elements made of a dense ceramic-metallic material which can produce furnace temperatures approaching 1800°C. Although more expensive than traditional metallic elements, MoSi2 elements are known for their longevity due in part to a protective quartz layer that forms on the surface of the element “hot zone” during operation. Duralite MoSi2 elements are made to industry standard established resistance values, dimensions and geometries, and therefore are interchangeable with other manufacturers of molybdenum disilicide elements. The key difference between Duralite MoSi2 and other MoSi2 suppliers is that Duralite MoSi2 elements are exceptionally priced. Duralite MoSi2 elements are graded in two maximum temperature ranges of 1700°C (3090°F) and 1800°C (3270°F). Elements are available in many shapes and forms (see examples shown below). Specifically, we offer the following MoSi2 styles: “U-shaped” (most common), “W-shaped”, and “Straight-shaped”, with or without right angle or oblique angle bends. Each element is specified by a “hot zone” diameter (d1) and length (Le), and a “cold zone” diameter (d2) and length (Lu).

Examples of typical MoSi2 element configurations.
3/6mm | d1=3mm | d2=6mm | A=25-30mm |
6/12mm | d1=6mm | d2=12mm | A=30-50mm |
7/14mm | d1=7mm | d2=14mm | A=30-50mm |
9/18mm | d1=9mm | d2=18mm | A=35-60mm |
12/24mm | d1=12mm | d2=24mm | A=60-100mm |
Benefits of MoSi2 elements include high temperature operation (in air), long element life and the ability in some cases to replace any failed elements hot.
Customers of Duralite MoSi2 elements enjoy two key added benefits – first, unparalleled price and second, experienced engineering support. Anyone can sell MoSi2, but knowing how to design the system is where Duralite excels. MoSi2 systems must be engineered for customer to get the best performance and optimum service life. Duralite engineers can assist in:
· analyzing the relationship between the furnace temperature, element temperature and the element surface load
· selecting the element surface load according to the furnace construction, atmosphere and operating temperature
· choosing the most suitable element size and style for your application
Physical Properties:
Bulk Density-g/cm3 | Bending Strength-MPa | Hardness-GPa | Compression Strength-MPa | Water Absorption-% | Heated Elongation-% |
5.8±0.1 | 450 | 11 | >1500 | ≤0.2% | 4 |
Different Working Temperature in Different Atmosphere.
Atmosphere | The Maximum Using Temperature of Element | |
1700 Grade | 1800 Grade | |
NO2,CO2,O2,Air | 1700°C | 1800°C |
He,Ar,Ne | 1650°C | 1750°C |
SO2 | 1600°C | 1700°C |
CO,H2 | 1500°C | 1600°C |
WetH2 | 1400°C | 1500°C |
DryH2 | 1350°C | 1450°C |